Essential Principles - LECTURES 1& 2
Introduction and General Overview: Terms, Naming, Pharmacodynamics, Pharmacokinetics, socioeconomic, genetic, gender and age-dependent variables, etc. Review of basic principles.
INTRODUCTORY LECTURE HANDOUT
This handout covers includes:
Resources for online drug information
Routes of Administration
Common generic suffixes
Common terms incld Allergic, Idiosyncratic, Black box, Summation, Synergism, etc.
Pharmacodynamics (PD) including:
Competitive, noncompetitive, reversible and irreversible receptor binding
Receptor specificity and subtypes
Therapeutic Index
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption (including) First Pass Metabolism
Distribution
Metabolism (P450 & conjugation)
Excretion
Half-life
Socio-cultural and demographic considerations
Pregnancy
Controlled Substances
Supplements
Drug study considerations
Abbreviations
Click the button above to download the handout.
PHARMACODYNAMICS
Videos and handouts to help you master pharmacodynamics, the study of the mechanism of actions of drugs.
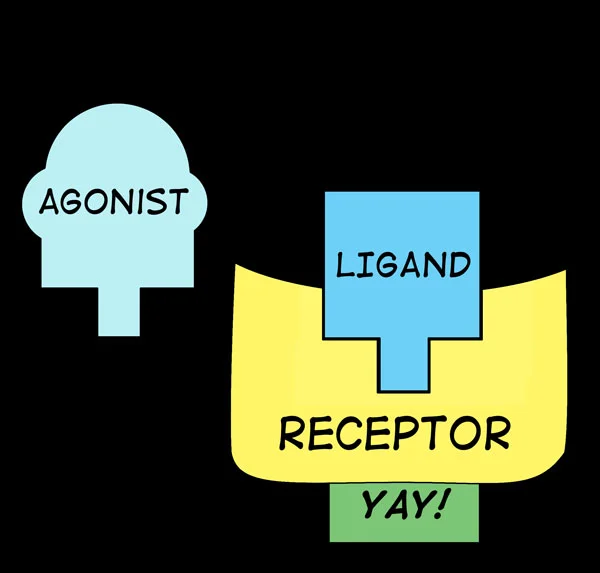
Introduction to Pharmacodynamics: Agonists, Antagonists and Receptors. The handout is the “First Lecture Handout” you can download at left. Objectives: 1. Explain the ways an enzyme-substrate complex is the same as a receptor-ligand complex. 2. Explain the differences between an enzyme-substrate complex and a receptor-ligand complex. 3. Define the terms: site of action, receptor, ligand, enzyme, substrate, agonist, antagonist, direct-acting 4.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Videos to help you master pharmacokinetics; that is not an easy task!!